The difference between home distillation and commercial distillation lies primarily in scale, equipment sophistication, regulatory compliance, and intended use. Here’s a breakdown of the key distinctions:
1. Scale and Capacity:
Home Distillation: Typically involves small-scale setups, often for personal use or hobbyist purposes. Equipment may include small pot stills or reflux stills capable of producing relatively small quantities of distilled spirits or essential oils at a time (e.g., liters per batch).
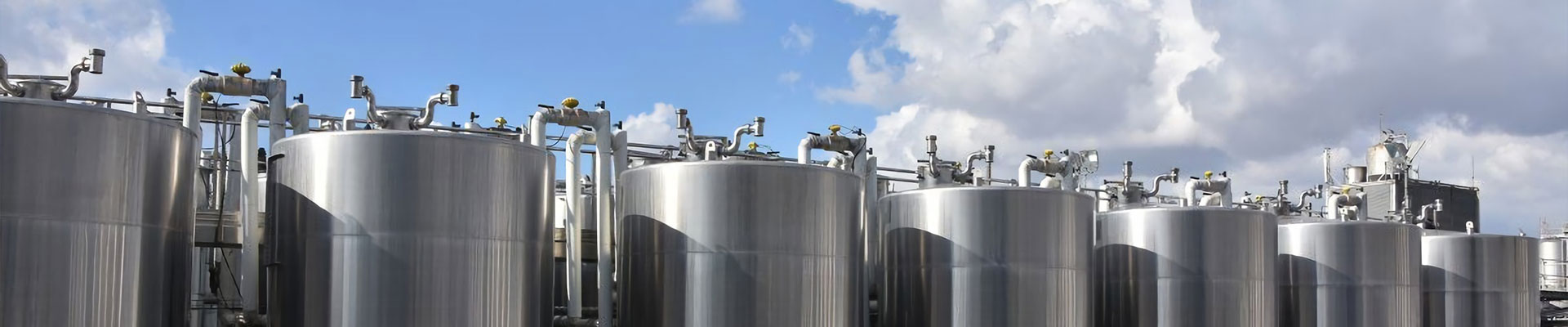
Commercial Distillation: Involves large-scale operations designed for industrial production. Commercial distilleries use larger and more advanced equipment, such as continuous column stills or multi-column distillation systems, capable of producing large volumes of alcohol or other distilled products (e.g., hundreds to thousands of liters per batch).
2. Equipment Sophistication:
Home Distillation: Equipment used at home is simpler and often manually operated. It may include basic pot stills, reflux stills, or similar designs that are easier to manage by individual operators.
Commercial Distillation: In commercial settings, distillation equipment is more sophisticated and automated. It includes features for precise control over temperature, pressure, reflux ratio, and other variables to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
3. Regulatory and Legal Considerations:
Home Distillation: In many countries, home distillation of alcohol for personal consumption is illegal or heavily regulated due to safety concerns and excise tax laws. Regulations may vary significantly by jurisdiction.
Commercial Distillation: Commercial distilleries must adhere to strict regulatory requirements concerning safety, hygiene, environmental impact, product labeling, and taxation. Compliance with these regulations is essential for legal operation.
4. Quality and Consistency:
Home Distillation: Quality and consistency can vary widely depending on the skills and experience of the individual operating the still. Factors such as temperature control, cuts (separation of heads, hearts, and tails), and equipment quality can impact the final product.
Commercial Distillation: Commercial distilleries focus on maintaining high product quality and consistency across batches. They invest in quality control measures, laboratory testing, and standardized processes to ensure that products meet consumer expectations and regulatory standards.
5. Intended Use and Market:
Home Distillation: Typically used for personal consumption, experimentation, or small-scale production of spirits, essential oils, or distilled water. It’s often a hobbyist pursuit or a means of producing specialty products.
Commercial Distillation: Products are intended for wider distribution and sale in markets such as alcoholic beverages, pharmaceuticals, perfumes, and industrial applications. Commercial distilleries operate as businesses, aiming for profitability and meeting market demand.
Summary:
While both home and commercial distillation involve the process of separating substances through evaporation and condensation, the scale, equipment complexity, regulatory framework, quality standards, and market focus differentiate them significantly. Home distillation tends to be more informal and restricted, whereas commercial distillation is a formalized, regulated industry with stringent requirements for production, quality control, and compliance.
Post time: Jul-04-2024